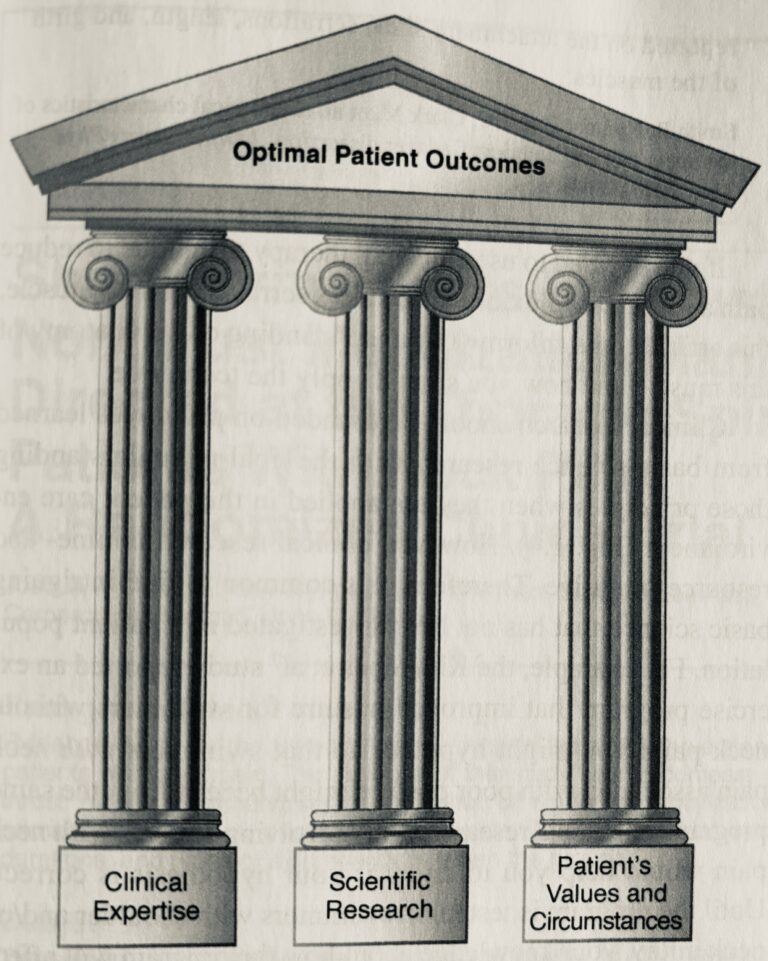
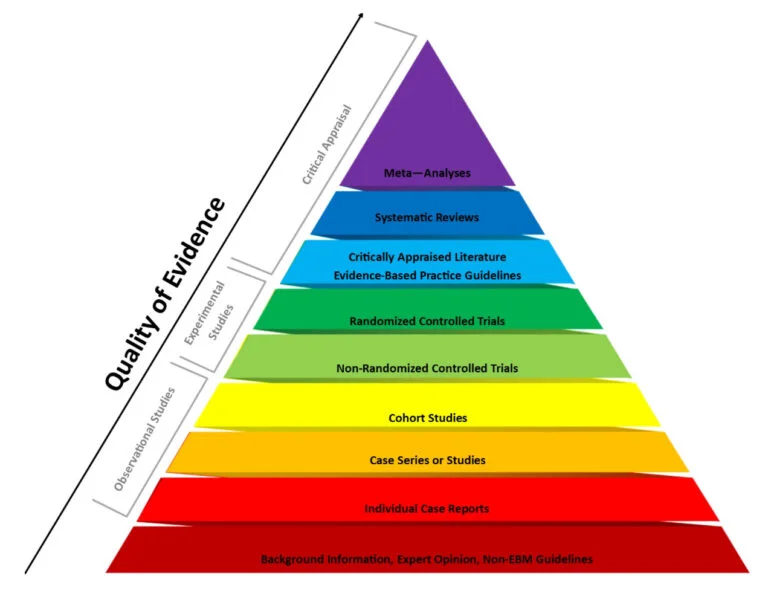
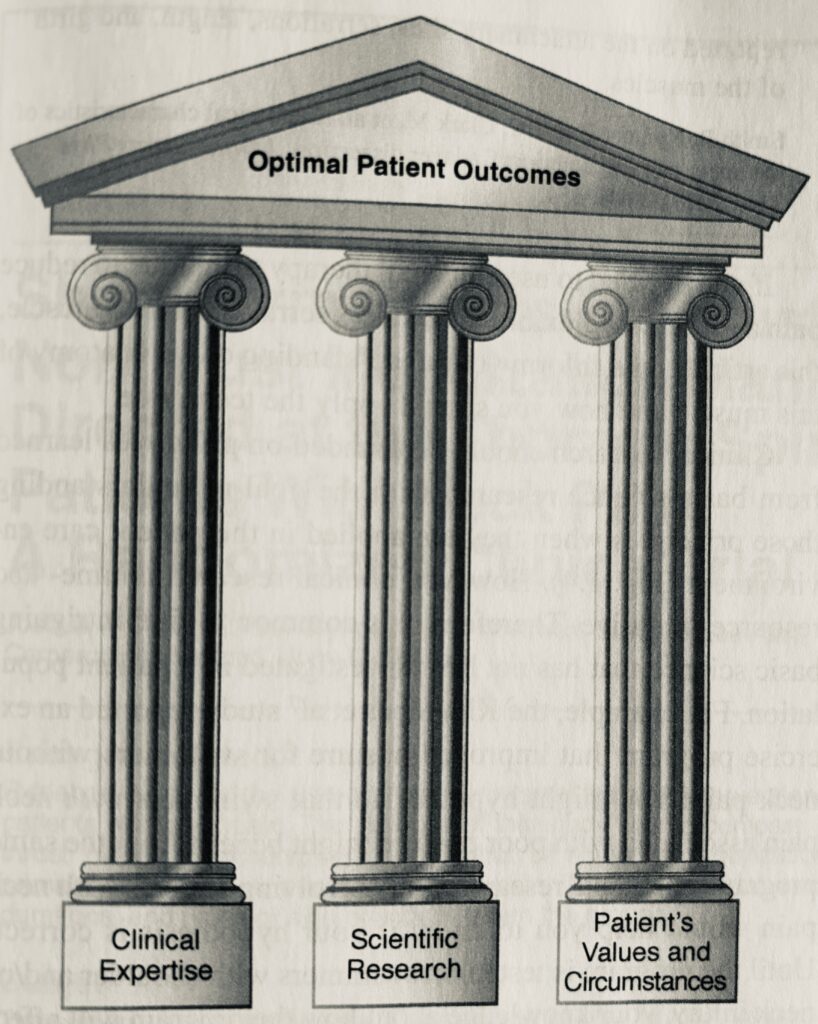
Clinical evidence is the backbone of modern medicine, offering a foundation for making informed healthcare decisions.
It encompasses data and findings derived from a variety of research methodologies, including clinical trials, observational studies, and meta-analyses.
This evidence serves as a crucial tool in evaluating the efficacy and safety of medical treatments, interventions, and diagnostic tools.
Definition of Clinical Evidence
In simple terms, clinical evidence consists of information obtained through systematic research that demonstrates how effective and safe a medical treatment or intervention is. This encompasses both quantitative and qualitative data collected from clinical trials, patient outcomes, and research studies.
Clinical evidence can be understood as applicable to an evidence based practice and can be contrasted with anecdotal evidence.
Healthy feet…great price!
- Fast shipping for $3-5
- Great variety
- Long-lasting quality
- Add lace-locks for quick changes

Try minimalist shoes from XeroShoes.com!
Contextual Application in Treatment Efficacy
The primary goal of clinical evidence in the context of treatment efficacy is to provide a robust basis for understanding how well a medical treatment works in real-world settings. It involves evaluating and comparing the outcomes of different treatments to determine the most effective and safe options for patients.
Examples of Clinical Evidence
To illustrate the application and importance of clinical evidence, consider the following examples:
- Comparative Studies: These research studies compare conventional treatments with new drug therapies for specific adult illnesses. They aim to identify any advancements in efficacy and safety that new treatments may offer over existing ones.
- Longitudinal Trials: Such trials analyze the impact of lifestyle changes on chronic disease progression over several years. They provide valuable insights into how modifications in diet, exercise, or behavior can influence disease outcomes.
- Meta-Analyses: By pooling data from multiple studies, meta-analyses evaluate the accuracy and reliability of various diagnostic tests. These analyses help establish standards for early disease detection tools.
- Observational Studies: These studies assess the safety and effectiveness of vaccines in preventing infectious diseases across different age groups. They are vital for understanding vaccine impact and addressing public health concerns.
In summary, clinical evidence plays a pivotal role in guiding healthcare professionals as they strive to offer the best possible care. By relying on well-conducted research and rigorous analysis, clinical evidence ensures that medical interventions are not only effective but also safe for patients.
To find out about bring more objectivity to your clinic, check out Best Handheld Dynamometer: Comparison & Review.
Sources
Buetow, Stephen, and Timothy Kenealy. “Evidence‐based medicine: the need for a new definition.” Journal of Evaluation in Clinical Practice 6.2 (2000): 85-92.
Fetters, Linda, and Julie Tilson. Evidence based physical therapy. FA Davis, 2018.
Rycroft‐Malone, Jo, Kate Seers, Angie Titchen, Gill Harvey, Alison Kitson, and Brendan McCormack. “What counts as evidence in evidence‐based practice?.” Journal of advanced nursing 47, no. 1 (2004): 81-90.
Spencer, Trina D., Ronnie Detrich, and Timothy A. Slocum. “Evidence-based practice: A framework for making effective decisions.” Education and treatment of children 35, no. 2 (2012): 127-151.
Titler, Marita G. “The evidence for evidence-based practice implementation.” Patient safety and quality: An evidence-based handbook for nurses (2008).