Massage guns have found their ways into many homes and offices, but do they have a place in a Pilates studio?
Let’s have a look at how a massage gun can deepen a Pilates practice. You’ll learn how teacher can use a massage gun with clients with diverse needs and abilities.
What’s a Massage Gun? (and how not to use it)
Massage guns create a high speed vibrational force at the click of a button. Applying vibration technology to health and fitness is not a new idea, but massage guns have now become very common.
And it’s no surprise why. For around $70, you can get some quick relief from muscle soreness.
But most people use massage guns in a way that is not very helpful long term: they pound a sore muscle until they can’t feel it any more. Now, this technique may get a muscle to release—i.e., no longer be held in spasm, but that’s not a long-term fix.
Plus, there are many other ways Pilates clients can benefit from a massage gun that will help them more than this temporary relief.
Why Use a Massage Gun for Pilates?
There are four reasons why a massage gun is useful for Pilates:
- Increasing muscle activity
- Improving body awareness
- Decreasing muscle activity
- Decreasing muscle soreness
Most people buy a massage gun because of #4, but research shows that’s the least important thing a massage gun can do for Pilates practitioners. Read below to find out why that is.
1. Massage guns increase muscle activity
Activating muscles via stimulation: there’s ongoing research showing that vibrations from a massage gun can activate muscles.
Research thus far suggests that massage guns stimulate receptors in muscles that tell your central nervous system when a muscle is contracting and how hard. Indirectly, this makes the muscle more able to contract, which means your client will be able to use the muscle more.
To stimulate a muscle, run the massage gun along its attachment points to the bones (i.e., origins and insertions) on a higher setting. Set the massage gun to be as rapid as the client can endure without causing any pain.
Example: Activate the gluteus medius
If you’ve been in a Pilates studio in your life, you’ve probably heard of the gluteus medius (or glute med). The glute med is primarily a stabilizer, helping you maintain your balance. Its primary functions are:
- Abduct the leg (moving it away from pelvis)
- Adduct the hip (moving it over the heel)
Although an important muscle for stability, the gluteus minimus is often under-active. According to research, running a massage gun at night speed along the glute med can send messages to the central nervous system that improve communication between the brain and muscle. That means the glute can receive message from the brain more easily to contract.
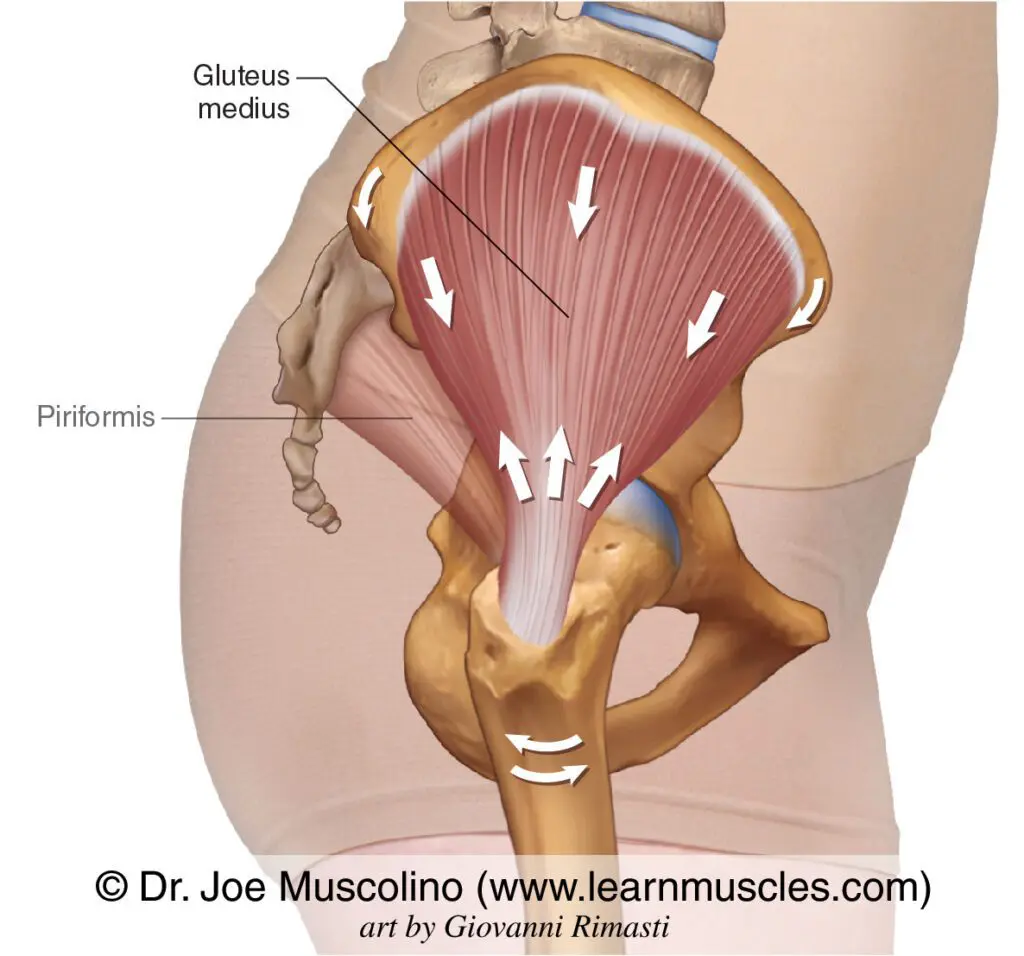
2. Improving body awareness
A massage gun can increase your body awareness in a few ways:
- By activating inactive muscles.
- By increasing awareness within the muscles. Evidence shows that vibration stimulates sensory neurons within a muscle. Specifically, it stimulates type Ia afferent neurons, which report the amount and rate of the change of length of a muscle (e.g., how far and how fast it is contracting).
Note that overuse of a massage gun can decrease proprioceptive awareness (and thereby balance). If you sit on a muscle until it is desensitized, it’s no surprise that it won’t send accurate information regarding its activity.
3. Decreasing Muscle Activity (muscle inhibition)
Much of your life in Pilates, particularly earlier, is occupied with trying not to use certain muscles. While instructors usually try various means such as verbal and tactile cuing or props to inhibit some muscles from engaging, massage guns can also do the trick.
This is by doing the activity most commonly used by massage gun owners: sitting on a muscle for a longer period of time.
4. Decreasing – and avoiding! – Muscle Soreness
Studies show that use of a massage gun following a workout can keep you out of pain. That’s great news, and a good way to keep up with your Pilates practice. While Pilates practitioners may not have much soreness after they’ve been training in Pilates for a few months, it’s common to be sore after the first few lessons.
Use of a massage gun immediately after a lesson is likely to decrease the likelihood of soreness (specifically, Delayed Onset Muscular Soreness (DOMS).
So, if you have a client who complains of significant muscle soreness (and then cancels sessions!), you might recommend a massage gun.
If you find especially sensitive points while using a massage gun, the Brookbush Institute recommends going over that point with a slower vibration speed with a smaller attachment.
Therapeutic benefits of massage guns
While it is not in our scope of practice as Pilates instructors to provide therapy, there are certainly therapeutic aspects of the Pilates method. Many Pilates studios have close relationships with physical therapists, where the PT will refer a patient to a Pilates instructor after they are cleared for movement.
Studies are showing that deconditioned muscles can be strengthened by use of vibration technology. Muscular deconditioning can be due to any kind of disuse, including being confined to a bed or a cast.
If you are referred a client 1) with a known issue who has been 2) cleared for movement, then a massage gun may be a helpful tool to maximize your time with your client.
Which Massage Gun is Best for Pilates?
There are tons of massage guns out there. After conducting a lot of research, I’ve learned that quality is not always equivalent to cost. Here are some features you’ll want to have in any massage gun in your studio or that you recommend to clients:
- Adjustable speed settings
- Multiple heads to choose from
- Quiet
- Reliable
- Cost-effective
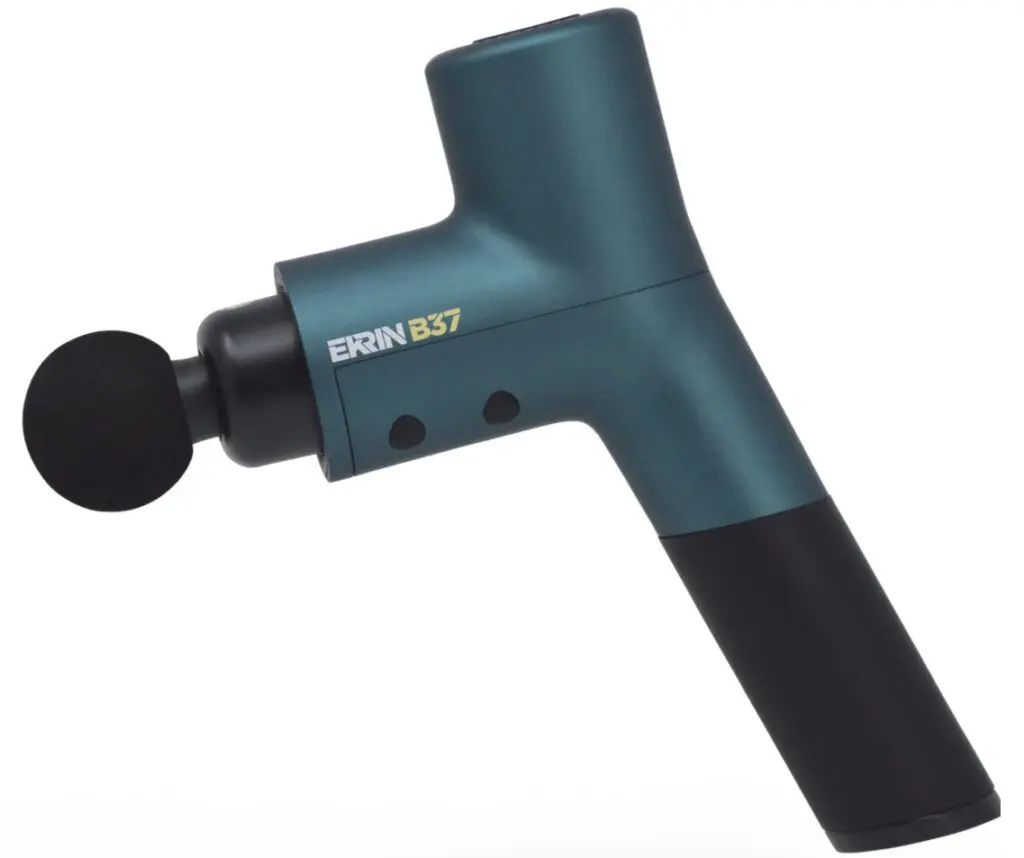
But despite a huge market, there is one massage gun (and one company) that I recommend hands down, and that’s the Erkin B37.

We recommend the B37 ($184 with VERSUS20 discount) over the more expensive B37S ($264 with discount) simply because the additional options aren’t likely worthwhile for Pilates practitioners.
(The B37S has pressure control sensor (hence the S). But this sensor really isn’t necessary for Pilates instructors, who should be aware of the pressure they’re exerting on a client’s body.)
On the other hand, the cheaper Erkin 365 does not allow you to control the speed of the vibration. Some clients will not like the factory setting of the Erkin 365 (they may want faster or slower), so you’ll want a model that allows you to control that.
If you’re recommending a model for home use, you might recommend the Erkin 365 or Bantam. Neither has adjustable speed, but they are easier to hold (and the Bantam is very portable).
Why we love Erkin’s massage guns
- Control over vibration speed: surprisingly, this is rare among massage guns. You may have clients who don’t like the higher speeds. There is also evidence that the speeds have different effects on muscles.
- Quiet: you won’t disturb other clients.
- Fast, free shipping from a small business.
- Lifetime warranty: this is nearly impossible to find among competitors, and demonstrates high reliability.
- Includes great case: that’s extra with other brands, including Hypervolt.
- Super customer service: lighting-fast replies to inquiries from actual people!
- Free gift with review: leave a review after your purchase, and get a free gift. I won’t say what, but I will say it is also high quality and very useful.
Discount code for Erkin Massage Guns: VERSUS20
Versus Pilates has an exclusive code for you to get 20% off your order (with free, fast shipping!) from Erkin. Just type in VERSUS20.
This code gives you 20% off your entire order! We receive a small commission of the sale if you use the coupon, so it’s also an easy way to express your gratitude if this post has been helpful for you.
How to get 20% off Erkin Massage Gun Products
- Go to your basket. There you’ll see all the items you selected to purchase.
2. Select “Check Out.” Then click “Add a discount code.”
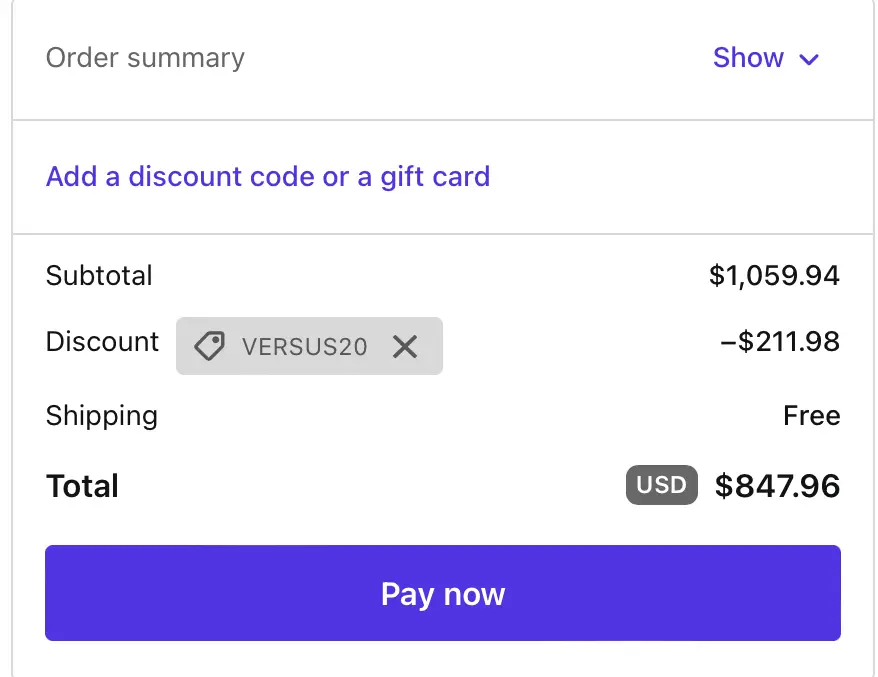
3. Enter VERSUS20 and see your 20% off applied immediately.
Sources
Some of the research presented here has been adapted from the Brookbush Institute’s article “The Effects of Local Vibration: Introduction to Vibration Release Techniques.“
- Pietrangelo, T., Mancinelli, R., Toniolo, L., Cancellara, L., Paoli, A., Puglielli, C., … & Di Tano, G. (2009). Effects of local vibrations on skeletal muscle trophism in elderly people: mechanical, cellular, and molecular events. International journal of molecular medicine, 24(4), 503-512.
- Iodice, P., Bellomo, R. G., Gialluca, G., Fanò, G., & Saggini, R. (2011). Acute and cumulative effects of focused high-frequency vibrations on the endocrine system and muscle strength. European journal of applied physiology, 111(6), 897-904.
- Koh, H. W., Cho, S. H., Kim, C. Y., Cho, B. J., Kim, J. W., & Bo, K. H. (2013). Effects of vibratory stimulations on maximal voluntary isometric contraction from delayed onset muscle soreness. Journal of physical therapy science, 25(9), 1093-1095.
- Gabriel, D. A., Basford, J. R., & An, K. N. (2002). Vibratory facilitation of strength in fatigued muscle. Archives of physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, 83(9), 1202-1205.
Vibration and soreness
- Iodice, P., Ripari, P., & Pezzulo, G. (2019). Local high-frequency vibration therapy following eccentric exercises reduces muscle soreness perception and posture alterations in elite athletes. European journal of applied physiology, 119(2), 539-549.
- Percival, S., Sims, D. T., & Stebbings, G. K. (2022). Local Vibration Therapy, Oxygen Resaturation Rate, and Muscle Strength After Exercise-Induced Muscle Damage. Journal of Athletic Training (Allen Press), 57(5).
- Sahebazamani, M., & Mohammadi, H. (2012). Influence of vibration on some of functional markers of delayed onset muscle soreness. International Journal of Applied Exercise Physiology, 1(2).
- Koeda, T., Ando, T., Inoue, T., Kamisaka, K., Tsukamoto, S., Torikawa, T., & Mizumura, K. (2003). A trial to evaluate experimentally induced delayed onset muscle soreness and its modulation by vibration. Environmental Medicine: annual report of the Research Institute of Environmental Medicine, Nagoya University, 47, 22-25.
Vibration and Rehabilitation
- Wang, H., Chandrashekhar, R., Rippetoe, J., & Ghazi, M. (2020). Focal Muscle Vibration for Stroke Rehabilitation: A Review of Vibration Parameters and Protocols. Applied Sciences, 10(22), 8270.